Is a Tomato a Fruit or Vegetable? Botanists and Traders Disagree.
Adults sometimes stop asking questions like “Is a tomato a fruit or a vegetable?” Recently, my middle school-aged daughter quizzed us over dinner on this. She knew the answer because one of her classmates had recently presented on the legal answer in debate class. I was bemused that it came down to a Supreme Court decision emanating from a customs dispute. Here’s the answer, and some trade trivia on which countries export the most tomatoes. Some of the up and comers are quite intriguing.
Nix v. Hedden
In a decision rendered on May 10, 1893, the Supreme Court handed down its answer to whether the tomato is a fruit or a vegetable. Under the Tariff Act of March 3, 1883, vegetables were assessed a tariff of 10 percent ad valorem. Fruits could be imported duty-free. In Nix v. Hedden, Mr. John Nix brought a case against Edward Hedden, a customs officer at the port of New York, seeking to recover duties he paid under protest on tomatoes imported from the West Indies. Nix had to prove the tomato should be considered a fruit for the purpose of determining the import duty.
In Commerce and Common Parlance
Nix’s counsel read from Webster’s Dictionary, Worcester’s Dictionary, and the Imperial Dictionary, all of which defined “fruit” as the seed of plants or that part of plants containing the seed, reinforcing the textbook categorization of the tomato as a fruit. (To the botanist or natural historian, that’s the final word. The tomato is a fruit of the vine.)
But then the court heard from longtime sellers of fruits and vegetables. The witnesses suggested, and the court agreed, that in the common language of consumers and sellers, tomatoes are considered more like other vegetables than fruits. As Justice Gray put it in his summary, “vegetables…are usually served at dinner in, with, or after the soup, fish, or meat, which constitute the principal part of the repast, and not, like fruits, generally as dessert.” To this day, tomatoes are classified as a vegetable in Chapter 7 of the U.S. Harmonized Tariff Schedule.
We Grow a Lot More Tomatoes Today
The United States is one of the world’s leading producers of tomatoes, second only to China. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, fresh and processed tomatoes generate more than $2 billion in annual U.S. farm cash receipts.
Every U.S. state produces fresh market tomatoes. About twenty produce at a commercial scale. California and Florida devote 30-40,000 acres each to fresh market tomato production – somewhere between two-thirds and three-fourths of production – followed by Virginia, Georgia, Ohio, Tennessee, North Carolina, New Jersey, and Michigan.
Trade Allows Us to Eat Tomatoes All Year
We grow a lot of tomatoes, but we also eat a lot of tomatoes. Commercial sales of fresh tomatoes in the United States are strongest in the spring when they aren’t competing with availability of local tomatoes. But we can enjoy fresh-market tomatoes all year-round because of imports. Mexico tends to fill in the seasonal supply gap for consumers in western U.S. states, and to a lesser degree in the east since Florida produces a winter crop. U.S. greenhouse and hydroponic tomatoes also make up some the difference, but generally, about one-third of the fresh tomatoes we consume are imported. Mexico also accounts for more than 70 percent of the U.S. import market for greenhouse tomatoes. Canada supplies another 27 percent.
Chapter 7 of the Tariff Schedule Again
Mexican producers are competitive with California and Florida producers in the U.S. market. Worried about imports from Mexico eating into their sales, U.S. tomato producers petitioned the U.S. Department of Commerce to investigate whether Mexican producers were selling fresh-market tomatoes in the U.S. market below fair market value, undercutting the U.S. price. The investigation was suspended when Mexico entered into a negotiated agreement in 1996 that required the majority of fresh-market tomatoes imported from Mexico to adhere to an agreed minimum price.
In subsequent and more recent revisions to that agreement, the types of tomatoes covered under the agreement expanded, the tomato season was split into two periods to cover the summer and winter seasons —each with a separate minimum price, and the floor price was increased. The period between July 1 and October 22 targets competition between California and Baja, Mexico. From October 23 to June 30, Mexican fresh-market tomatoes must meet a higher minimum price to address competition between Florida and Sinaloa, Mexico. While we don’t impose duties on imports from our free trade agreement partners, the general duty for imports from other countries also varies depending on when in the growing season the tomatoes are imported. Either way, it’s the American consumer that foots the bill of the higher prices.
Outside North America, Azerbaijan is a Fast Grower
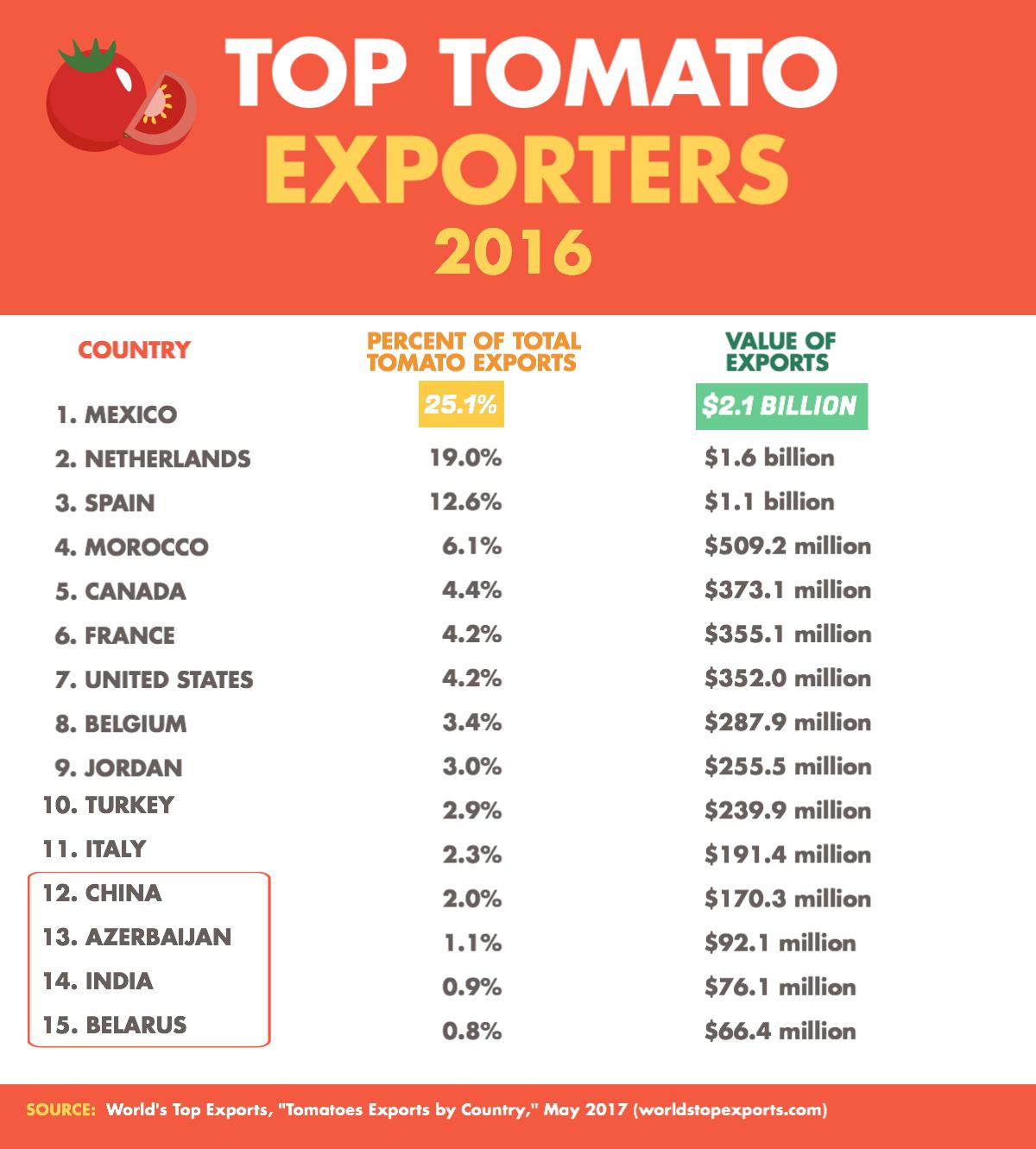
American fresh-tomato growers typically export 6 to 7 percent of their supply. About three-fourths of those exports go to Canada. U.S. exports to Mexico are a distant second. While American, Mexican — and to a lesser extent – Canadian, growers battle for North American market share, these fifteen countries globally exported the highest values of tomatoes during 2016, accounting for over 92 percent of global trade in tomatoes.
What might surprise you the most is the last four on this list. At number 13, Azerbaijan’s exports have grown 380 percent since 2012. China’s exports grew over that period by 119 percent, Belarus by 55.5 percent, and India grew its tomato exports by 42 percent.
Andrea Durkin is the Editor-in-Chief of TradeVistas and Founder of Sparkplug, LLC. Ms. Durkin previously served as a U.S. Government trade negotiator and has proudly taught international trade policy and negotiations for the last fourteen years as an Adjunct Professor at Georgetown University’s Master of Science in Foreign Service program.

